General Information
Strain Name | B6.Cg-Tg(tetO-Alb-uPA) /Vst |
Common Name | Tet-uPATg; B6.Tet-uPA |
Origin | Beijing Vitalstar Biotechnology Co., Ltd. |
Background | C57BL/6NCrl |
Coat color | Black |
Development
Tet-uPA mice are liver-specific expression of Alb promoter/enhancer-driven rtTA gene and TRE-uPA gene fragments were transferred into mice to establish Tet-On regulated uPA transgenic mice, which are induced by Dox to express uPA in the liver, which can cause liver injury.
TRE-uPA transgenic mice and Alb-rtTA transgenic mice were first constructed and mated to obtain Alb-rtTA/TRE-uPA double-positive mice, in which uPA expression and liver injury were detected by Dox induction [1]. Subsequently, Alb-rtTA/TRE-uPA double-positive mice were backcrossed to C57BL/6NCrl for 8 consecutive generations to obtain Tet-uPA B6 mice.
The advantage of Tet-uPA mice is that the mice are healthy when uninduced and develop liver injury only when induced by Dox administration, and the extent of liver injury can be controlled by the dose of Dox. Feeding a high-fat or high-fat-high-sugar diet for 2-3 months combined with Dox induction for 2 months resulted in hepatic steatosis within 8 weeks, steatohepatitis within 16-24 weeks, and HCC (primary hepatocellular carcinoma) in 90% of the mice after 30-50 weeks.
Phenotype
1. B6.Tet-uPA mice injected with Dox (100 mg/kg) serum ALT/AST
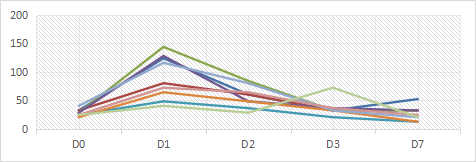
Fig 1. B6.Tet-uPA mice injected with Dox (100 mg/kg) serum ALT/AST
2. B6.Tet-uPA induces a human-like model of MASH
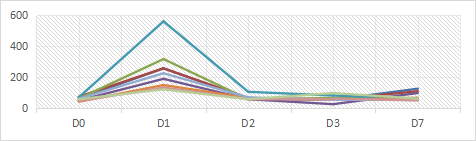
Fig 2. B6. tet-uPA induced liver injury and HDF feeding for 3 months induces a human-like model of MASH
3. Body weight curve of B6.Tet-uPA mouse
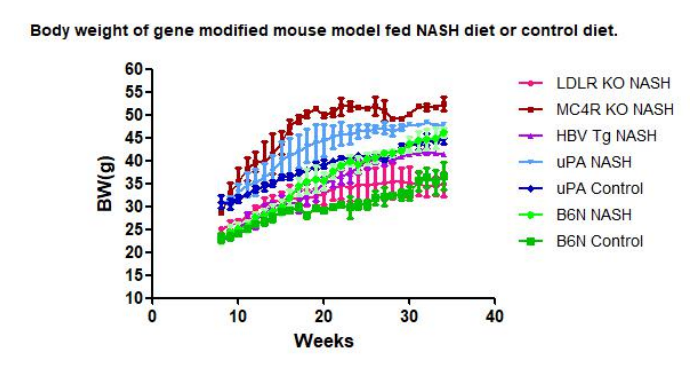
Fig. 3. Growth curve of B6.Tet-uPA fed NASH diets
4. B6.Tet-uPA mice liver HE and Sirius scarlet staining analysis
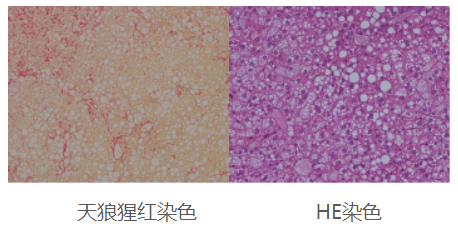
B6.Tet-uPA Mice Applications
1. Acute and chronic liver injury modeling and other related researches
2. Research on MASH model, liver cancer model, and drug safety evaluation, etc.
References
1. Song X J, et al. A Mouse Model of Inducible Liver Injury Caused by Tet-On Regulated Urokinase for Studies of Hepatocyte Transplantation. Am J Pathol. 2009, 175(5):1975-1983.

 animalmodel@vital-bj.com
animalmodel@vital-bj.com +8610-84928167
+8610-84928167