General Information
Strain Name | B6- Apoeem1/Vst |
Common Name | Apoe KO mice |
Origin | Beijing Vitalstar Biotechnology Co., Ltd. |
Background | C57BL/6N |
Coat color | Black |
Edited Gene | ApoE |
Development
Apoe (apolipoprotein E) encodes apolipoprotein E, which is a component of very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL), and mediates the transport and metabolism of cholesterol. Studies have shown that compared to wild-type mice, Apoe-/- mice have significantly higher cholesterol levels in their plasma. Due to the accumulation of cholesterol, fatty streaks appear near the aorta at around three months of age, which intensify with age, leading to pre-atherosclerotic lesions. The Apoe-/- model does not express Apoe protein, has significantly elevated blood lipid concentrations, and develops early atherosclerosis when fed a high-fat diet.
Apoe gene knockout mice were obtained using the CRISPR/Cas9-based gene editing technology. The detailed process is as follows: sgRNAs were designed in the 5'UTR and 3'UTR, where they cleave double-stranded DNA sequences, causing double-strand DNA breaks. The breaks are repaired using non-homologous end joining, ultimately resulting in a mouse model with the Apoe gene knocked out. A schematic diagram of the model construction is shown in Figure 1.
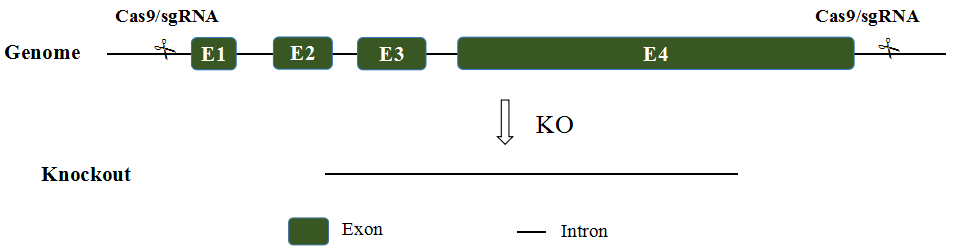
Fig 1. Schematic diagram of Apoe-/- mice production
Phenotype
1. Blood lipid levels
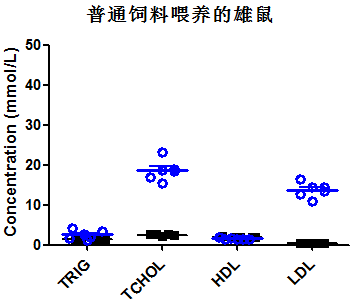
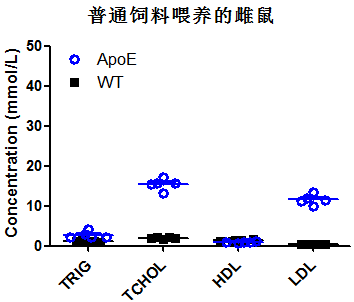
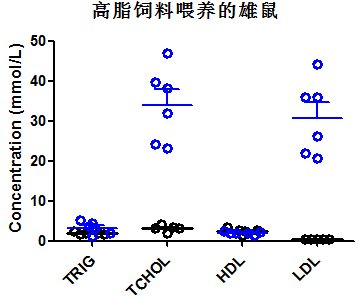
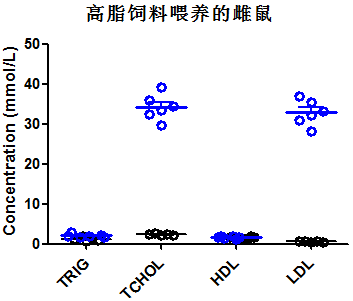
Fig 2. Lipid assay in wild-type mice and Apoe-/- mice
Note:TRIG:Triglyceride;TCHOL:Total Cholesterol;HDL:High-density lipoprotein;LDL:Low Density Lipoprotein
Four-week-old mice (male and female) were randomly divided into 2 groups, one group fed a normal diet and the other group fed a high-fat diet. After 10 weeks of feeding, collection of venous blood for lipid-related markers. Regardless of whether they were fed a high-fat diet or a normal diet, the concentrations of triglycerides and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) in Apoe-/- mice were significantly higher than those in wild-type mice; the concentrations of triglycerides and LDL in Apoe-/- mice fed a high-fat diet were higher than those in Apoe-/- mice fed a normal diet.
2. Macroscopic oil red O staining of aorta
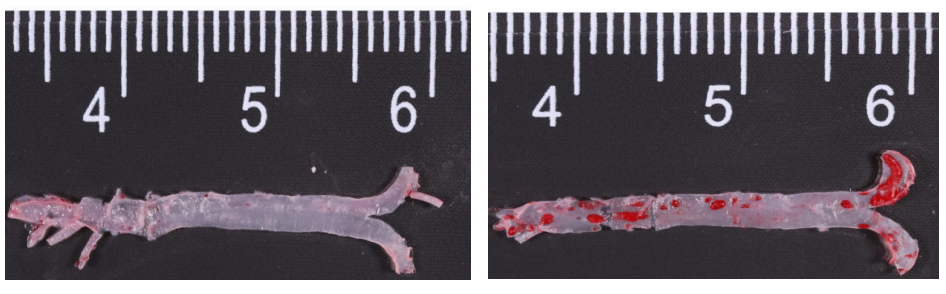
Fig 3. Macroscopic oil red O staining of aorta. Left: undiet-induced control mice; right: high-fat diet-induced Apoe-/- mice.
3. Oil red O staining of the aortic root
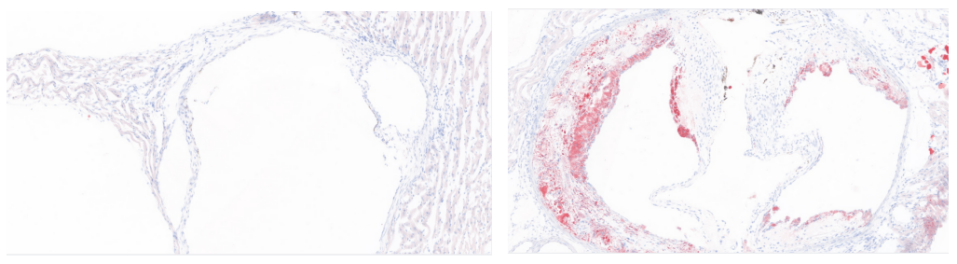
Fig 4. Oil red O staining of aortic root. Left: undiet-induced control mice; right: high-fat diet-induced Apoe-/- mice.
Apoe KO Mice Applications
1. Research on cardiovascular diseases: hypercholesterolemia, hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis, etc.
2. Research on body metabolic mechanism: fat and cholesterol metabolism research
3. Research on neurodegenerative diseases: Alzheimer's disease
Reference
1. 欧海龙,张礼林,何晓兰,等. ApoE-/-小鼠动脉粥样硬化模型的建立. 生命科学研究. 2015, 19: 141-144.
2. Plump AS, Smith JD, Hayek T, et al. Severe hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice created by homologous recombination in ES cells. Cell. 1992, 71(2):343-353.
3. Zhang SH, Reddick RL, Burkey B, et al. Diet-induced atherosclerosis in mice heterozygous and homozygous for apolipoprotein E gene disruption. J Clin Invest. 1994, 94: 937-945.
4. Shi Y, Yamada K, Liddelow SA, et al. ApoE4 markedly exacerbates tau-mediated neurodegeneration in a mouse model of tauopathy. Nature. 2017, 549(7673): 523-527.

 animalmodel@vital-bj.com
animalmodel@vital-bj.com +8610-84928167
+8610-84928167