General Information
Strain Name | HBV-Hu-URG |
Origin | Beijing Vitalstar Biotechnology Co., Ltd. |
Background | NOD |
Coat color | Albino |
Development
HBV-HuURG is a model of HBV-infected humanized liver mice.
Human-mouse chimeric liver mice (humanized liver mice) generated from URG mice transplanted with human primary hepatocytes can be infected by HBV viruses derived from hepatitis B patients or prepared in vitro. The natural process of HBV infection and replication can be recapitulated due to the presence of human hepatocytes in the mouse liver and the presence of cccDNA in the hepatocytes. Compared with HBV-Tg mice or AAV-HBV mice, HBV-HuURG mice are a true HBV infection model, which is of greater value in the study of the mechanism of HBV infection and the development of anti-HBV drugs.
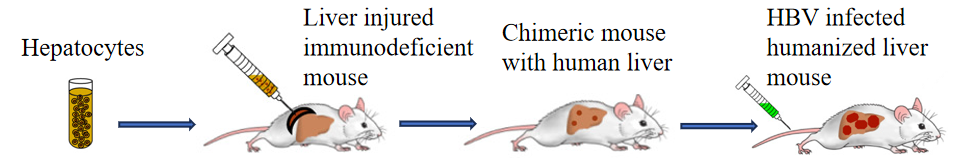
Fig 1. Schematic diagram of HBV-infected Hu-URG mice
Phenotype
1. Indicators of HBV at different times of infection with HBV type A virus
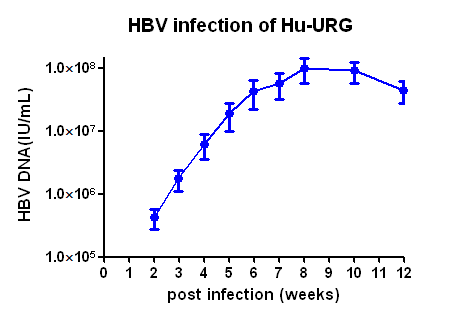
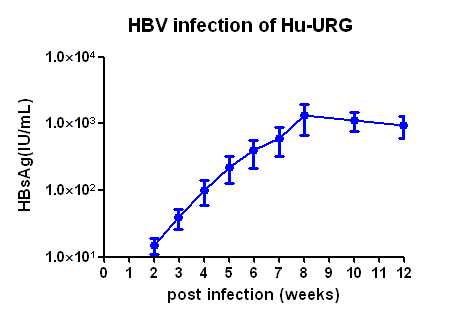
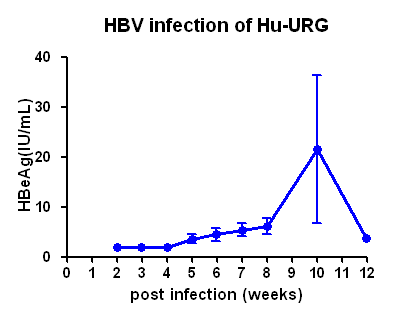
Fig 2. HBV-Hu-URG mice peripheral blood HBV indicators detection
2. Human Hepatocyte Reconstruction Levels
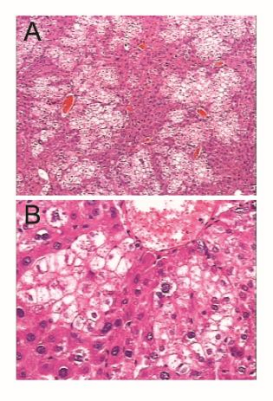
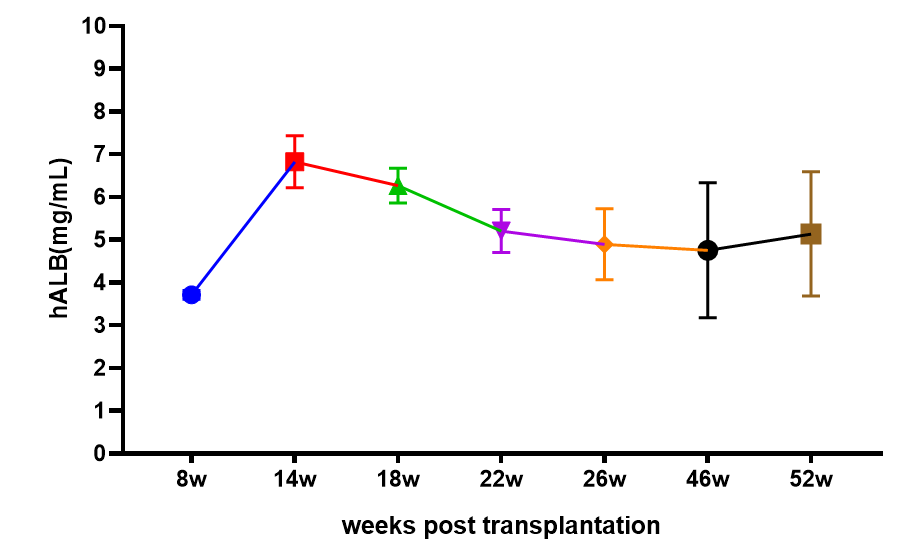
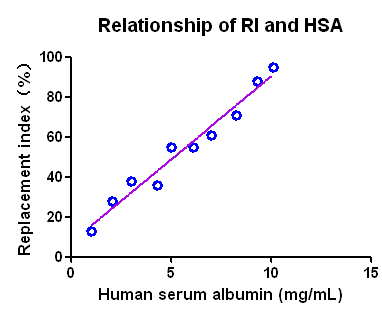
Fig 3. Human Hepatocyte Reconstruction Levels
Note: (A,B) HE staining demonstrated that human hepatocytes were successfully reconstituted in the livers of Hu-URG mice, and the lighter-stained parts were human hepatocytes; (C) peripheral blood human Alb levels of Hu-URG; (D) correlation analysis between peripheral blood Alb levels and the degree of chimerism of human hepatocytes in Hu-URG
The results showed that the human Alb level of Hu-URG mice was higher than 3 mg/mL for 52 weeks after HBV infection, and they could be infected with HBV virus at any time during this cycle, with an experimental window of up to 52 weeks.
3. Serum HBV DNA copy number and liver tissue indices in HuURG mice infected with different genotypes of HBV
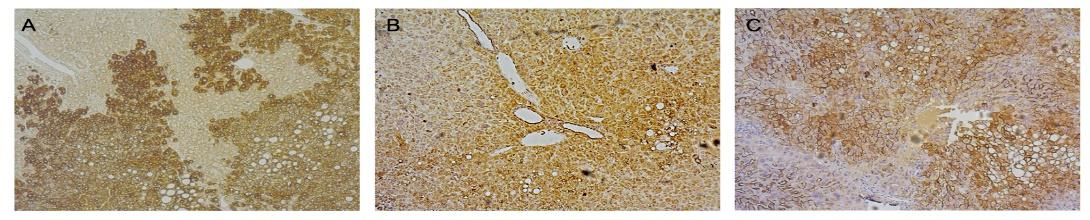
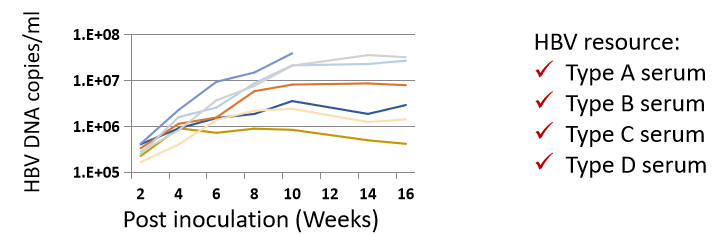
Figure 4. Serum and liver tissue indexes of HuURG mice infected with different genotypes of HBV.
Note: A is Human CK18, B is HBcAg, C is HBsAg
Examples of HBV infection and drug efficacy studies in Hu-URG mice
1. Hu-URG was used to study the antiviral activity of small molecule compounds in HBV patients after serum infection Potential mechanisms of influence on cccDNA transcription[1]
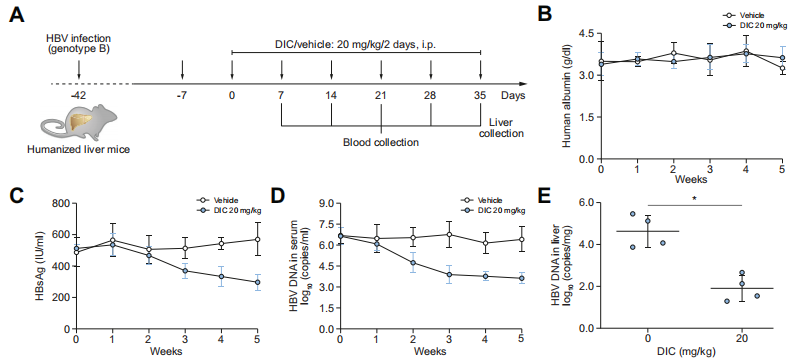
Fig5. Antiviral activity of Dicoumarol on HBV-infected Hu-URG mice
Hu-URG® mice (n=4/group) were injected intravenously with 50 μL of HBV patient serum (genotype B, 5.12×106 copies/mL). 20 mg/kg Dicoumarol was injected intraperitoneally on every other day for 6 weeks, while a control group was set up. Blood was taken weekly from the orbital venous sinus. The mice were executed after 35 d of drug administration, and liver tissues were collected for analysis. The results showed that the serum Alb of Hu-URG mice was consistently high. It was higher than 3 mg/mL during the 5 weeks of Dicoumarol administration, which was not significantly different from that of the control group.Dicoumarol treatment was effective in decreasing serum HBsAg and HBV DNA levels, as well as decreasing intrahepatic HBV DNA and HBV RNAs levels.
2. Hu-URG mice were used to study the antiviral activity of compound after infection of cultured HBV virus particles and its effect on cccDNA transcription[2]
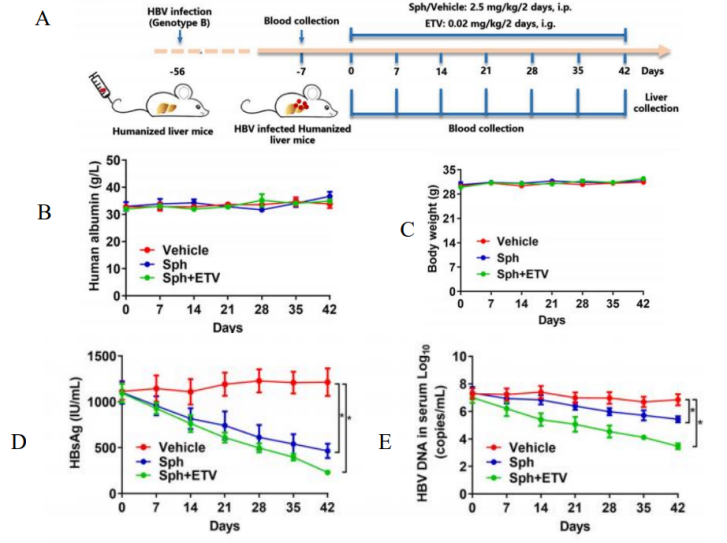
Fig 6. Antiviral activity of Sphondin against HBV-infected Hu-URG mice
Hu-URG® mice (n=4/group) were injected intravenously with patient serum (genotype B). 8 weeks later, the mice were randomly divided into a control group, a sphondin monotherapy group, and an ETV+sphondin combination group, and were administered and sampled according to the design as shown. The results showed that human Alb in the serum of Hu-URG® mice was consistently at a high level. higher than 3 mg/mL for 6 weeks of the administered treatments alone or in combination, which was not significantly different from the control group. The administration treatments also had no significant effect on body weight. sphondin treatment resulted in a significant reduction in serum HBsAg and HBV DNA. It also significantly reduced intrahepatic total HBV RNA, 3.5 kb RNA, HBsAg and HBx protein levels.
3. Hu-URG was used to investigate HBx enhancement of HBV replication through DDB1-mediated degradation of WDR77 in the liver[3]
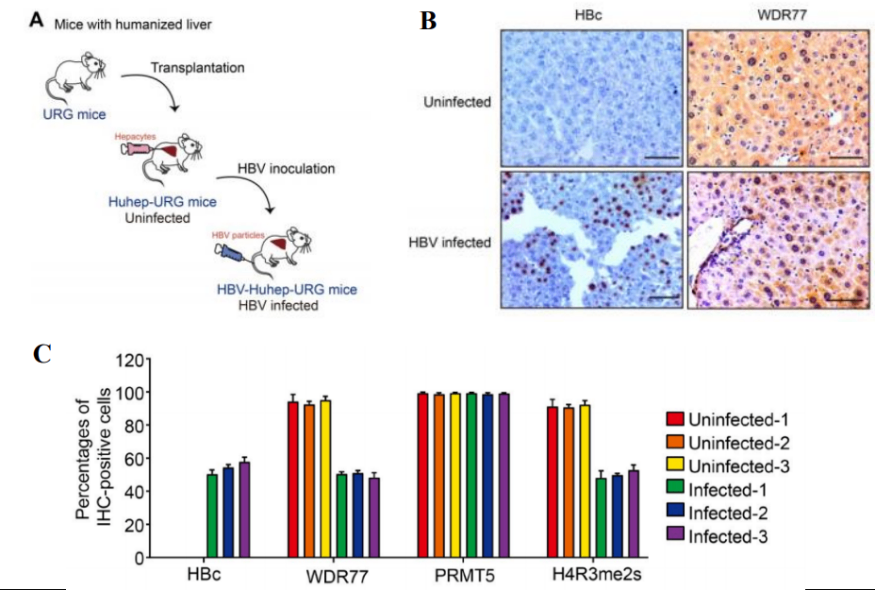
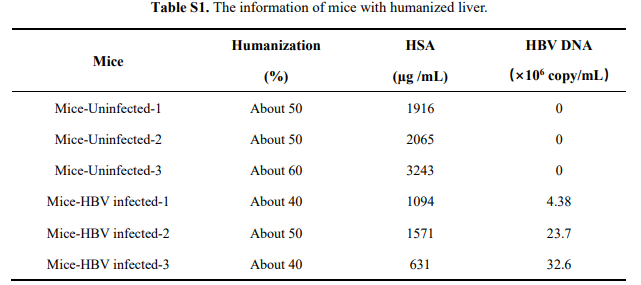
Fig7. HBV infection results in decreased WDR77 levels
PHHs were injected into 3-week-old URG® mice (n=3/group) by intrasplenic injection, and serum human Alb was measured by ELISA to assess the implantation and viability of PHHs. The mice were then infected with 2.5 × 108 IU/mL (0.2 mL/each) HBV pellets, and the mice were executed after 8 weeks. The results showed that Hu-URG® mice had high levels of Alb in serum and could be normally infected with HBV, and HBV infection and HBx expression significantly reduced the protein level of WDR77 of Hu-URG®, which in turn limited cccDNA transcription and HBV replication.
4. Hu-URG is used to investigate potential targets for drug treatment of HBV[4]
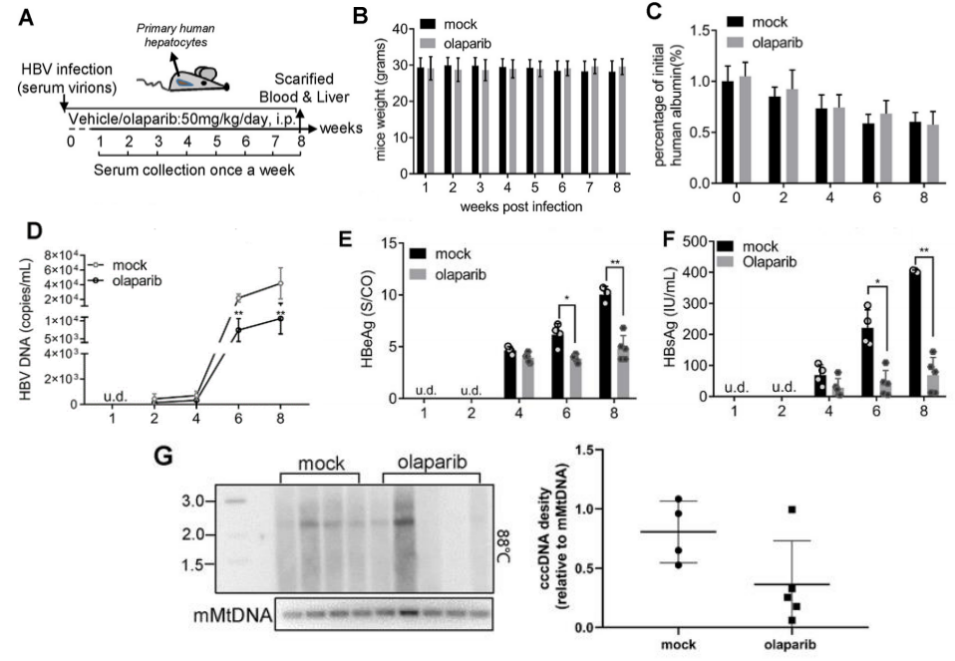
Fig8. Decreased HBV cccDNA in Hu-URG mice treated with PARP1 inhibitor (olaparib)
Nine male mice (n=4 male mice in mock group, n=5 male mice in olaparib group) were injected intravenously with 50 μL (5×108 copies/mL) of HBV patient serum. The diluted PARP1 inhibitor olaparib was administered intraperitoneally at a dose of 50 mg/kg per day 12 h after HBV infection. results showed that there was no significant difference in body weight and serum human Alb levels between the DMSO and olaparib groups for Hu-URG®. Administration resulted in a significant reduction in serum HBV DNA, HBsAg and HBeAg levels. Intrahepatic HBV cccDNA levels were reduced by half. These data suggest that olaparib reduces HBV replication and cccDNA formation in vivo.
5. Hu-URG was used to study the pathway of IFN-α-mediated HDAC3 inhibition of HBV transcription and replication[5]
Fig9. HDAC3 mediates inhibition of HBV transcription and replication.
Primary human hepatocytes (PHH) were transplanted into 3-week-old (n=5 each group, male and female) URG® mice to construct the resulting Hu-URG® mice. The Hu-URG® mice were then infected with 5.0 × 108 IU/mL (0.2 mL/mouse) HBV particles from HepAD38 cell supernatant. The results showed that human liver chimeric mice had a high level of Alb in serum and could be normally infected with HBV. HDAC3 mRNA levels in HBV-infected Hu-URG® mice were significantly lower than those in the control group, and Western blot analysis confirmed that the level of histone H4K8 2-hydroxyisobutyrylation was obviously enhanced. -URG® mouse livers with HBV cccDNA, suggesting that HDAC3 is anchored to the HBV cccDNA chromosome. In this study, we found that IFN-α inhibits HBV transcription and replication by promoting HDAC3-mediated de-2-hydroxyisobutyrylation of histone H4K8 on the hepatic HBV cccDNA chromosome.
HBV-Hu-URG® Mice Applications
1. HBV-Hu-URG mice can be used to study HBV drug safety assessment and human-specific liver metabolizing enzyme-related studies
2. HBV, HCV infection and antiviral activity signaling pathway studies
3. Drug metabolism and pharmacokinetics, efficacy studies
4. Stem cell research
5. Gene therapy
References
1. Cheng ST, et al. Dicoumarol, an NQO1 inhibitor, blocks cccDNA transcription by promoting degradation of HBx. J Hepatol. 2021, 74:522-534.
2. Ren F, et al. Sphondin efficiently blocks HBsAg production and cccDNA transcription through promoting HBx degradation. J Med Virol. 2023, 95:e28578.
3. Yuan H, et al. HBx represses WDR77 to enhance HBV replication by DDB1-mediated WDR77 degradation in the liver. Theranostics. 2021, 11(17):8362-8378.
4. Chen Y, et al. DNA Repair Factor Poly (ADP-Ribose) Polymerase 1 Is a Proviral Factor in Hepatitis B Virus Covalently Closed Circular DNA Formation. J Virol. 2022, 96(13):e0058522.
5. Zhao LN, et al. IFN-α inhibits HBV transcription and replication by promoting HDAC3-mediated de-2-hydroxyisobutyrylation of histone H4K8 on HBV cccDNA minichromosome in liver. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2022, 43(6):1484-1494.

 animalmodel@vital-bj.com
animalmodel@vital-bj.com +8610-84928167
+8610-84928167