General Information
Strain Name | HuHSC-NPG-hIL2 |
Origin | Beijing Vitalstar Biotechnology Co., Ltd. |
Background | NPG |
Coat Color | Albino |
Development
Linearized human IL-2 expression sequences were injected into the prokaryotic nuclei of NPG mice using a transgenic approach, and positive mice with appropriate expression (1000 pg/ml) were screened among the obtained progeny for production as breeders. In an isolator, commercial hIL-2 NPG mouse lines were established by inbreeding according to inbreeding expansion.
Human HSC transplanted into this mouse form a mouse known as HuHSC-hIL2-NPG, which promotes differentiation toward human NK cells. High levels of hIL2 can amplify the toxic effects of T cells, so this model can (1) accurately predict the efficacy of PD1 therapy and TILs therapy in the clinic; (2) effectively predict the inhibitory effects of TCR-T and CAR-T on solid tumors, and the anti-tumor effects are positively correlated with the expression of IL2.
Phenotype
1. Engraftment of human HSCs in NPG-hIL2 mice to reconstitute human NK cell
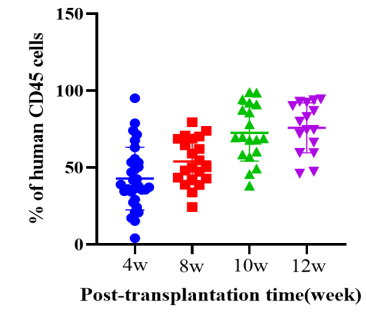
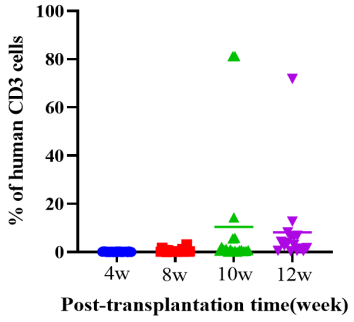
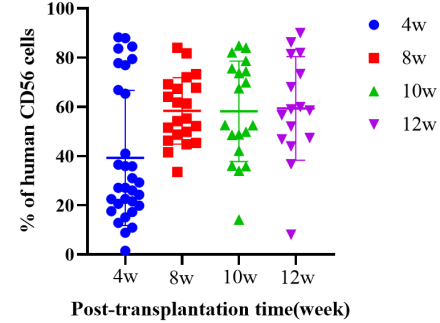
Fig1. Engraftment of human HSCs in NPG-hIL2 mice to reconstitute human immune system
After transplantation of CD34+ cells into hIL-2 NPG mice, the proportion of hCD45+ cells increases rapidly and remains at a high level even when observed at 12 weeks post-transplantation. A significant reconstruction of NK cells can be observed as early as 4 weeks post-transplantation, and this high level is maintained from weeks 8 to 12. It can be concluded that transplantation of HSCs in hIL2-NPG mice primarily promotes the reconstruction of human NK cells, while the levels of CD3+ T cells are relatively low.
2. Proliferation of purified NK cells after transplantation in hIL2-NPG mice
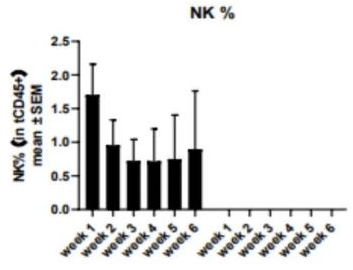
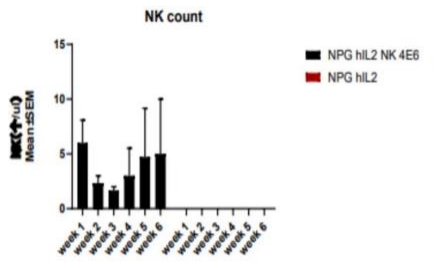
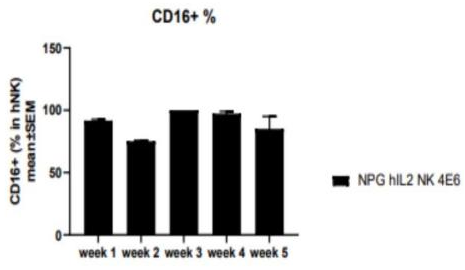
Fig2. Proliferation of purified NK cells after transplantation in hIL2-NPG mice
NK cells isolated from adult PBMCs transplanted into hIL2-NPG mice can stably maintain and proliferate in these mice
HuHSC-NPG-hIL2 Mice Applications
1. Research on NK function and evaluation of the efficacy of antitumor and antiviral effects (e.g., ADCC effects) through NK cell function
2. Cancer treatment (e.g., lysovirus and Car-T, etc.)
3. Inoculation of human tumors for screening of relevant drugs
4. Human cell and tissue transplantation
5. Immunity, hematopoietic transplantation and reconstruction
6. Regenerative medicine
7.Infectious diseases
Reference
1. Katano I, Takahashi T, Ito R, Kamisako T, Mizusawa T, Ka Y, Ogura T, Suemizu H, Kawakami Y, Ito M. (2015) Predominant development of mature and functional human NK cells in a novel human IL-2-producing transgenic NOG mouse. J Immunol. 194(7):3513-25.

 animalmodel@vital-bj.com
animalmodel@vital-bj.com +8610-84928167
+8610-84928167