General Information
Strain Name | HuPBMC-NPG |
Origin | Beijing Vitalstar Biotechnology Co., Ltd. |
Background | NPG |
Coat Color | Albino |
Development
HuPBMC-NPG is a model of NPG mice transplanted with human adult peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC). Because the transplanted PBMC contain mature immune cells, certain in vivo experiments requiring the presence of human immune function can be performed. The human-derived cells in the PBMC transplantation model are mainly T cells. Since the transplanted human-derived immune cells are mainly T cells, they will produce immune attack on the recipient mice to develop graft-versus-host disease (GvHD), so the PBMC model is available for experiments with a shorter window period, with a survival cycle of about 5-7 weeks, and relatively shorter dosing cycles. At the same time, the model can be used to evaluate GvHD drugs.
Phenotype
1. Engraftment of human peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) in NPG mice to reconstitute human immune system
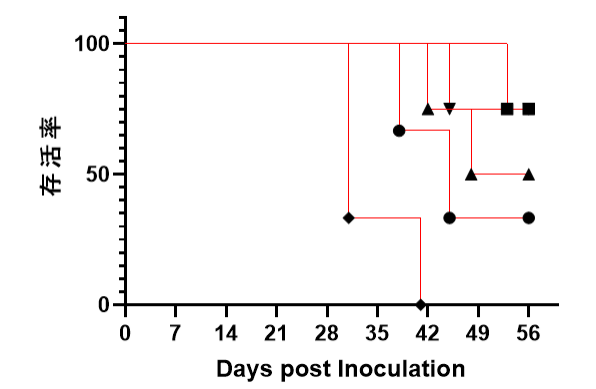
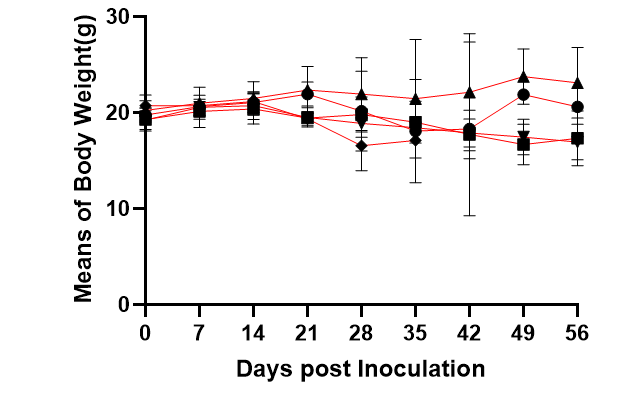
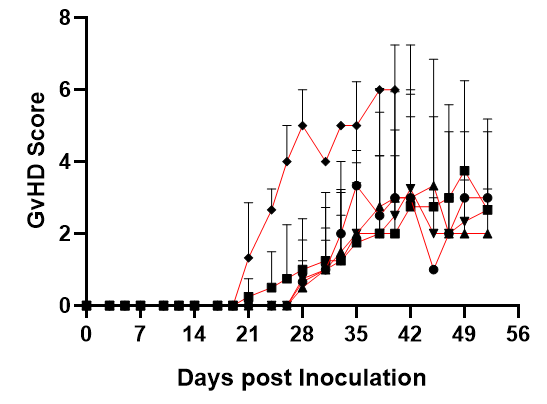
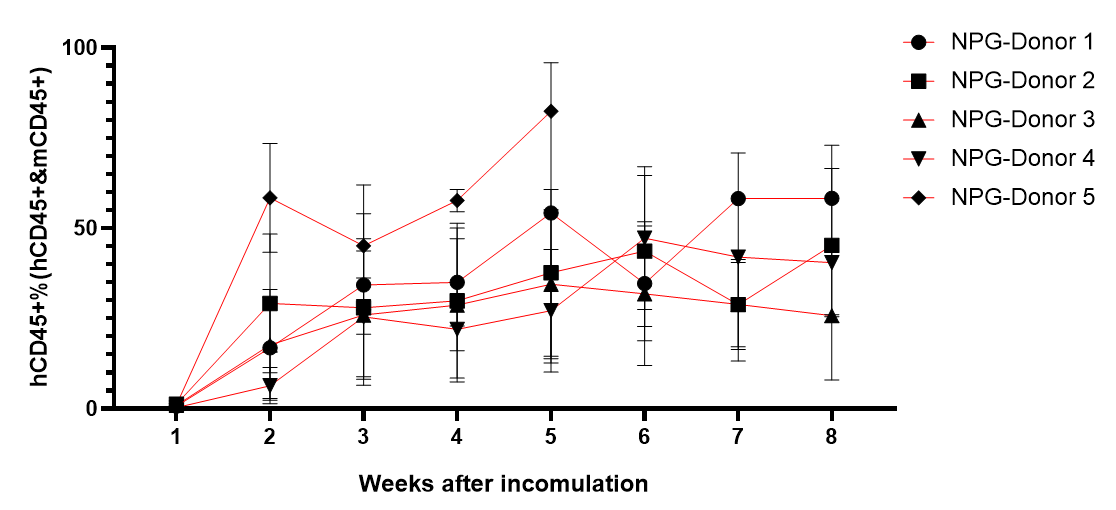
Fig1. Survival rates, body weight, GvHD scores, and levels of reconstitution following transplantation of human PBMC from different donors (5×106).
huPBMC from five different donors were injected into NPG mice, respectively; high levels of hCD45+ cells were produced 2 weeks after injection and could be maintained up to about 8 weeks; and it was found that GvHD and deaths occurred one month, which shortened the window of use of Hu-PBMC-NPG mice.
2. The GVHD response of HuPBMC-NPG[1]
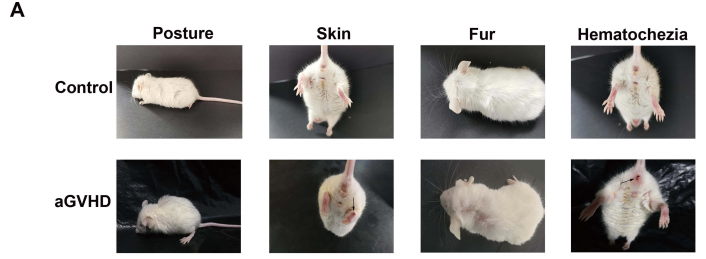
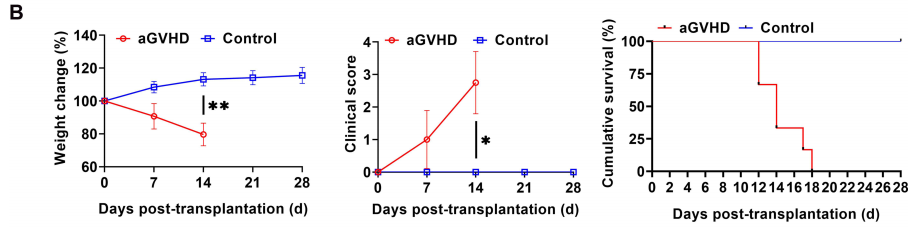
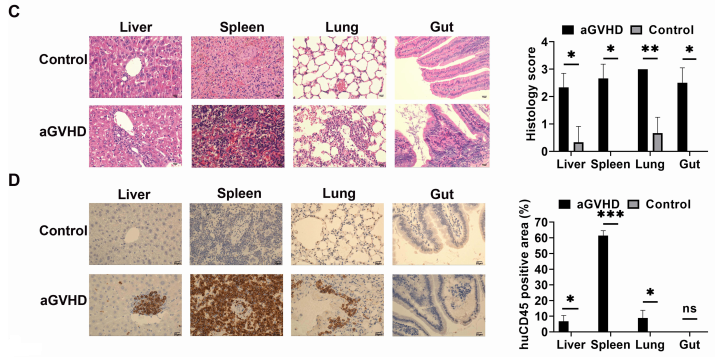
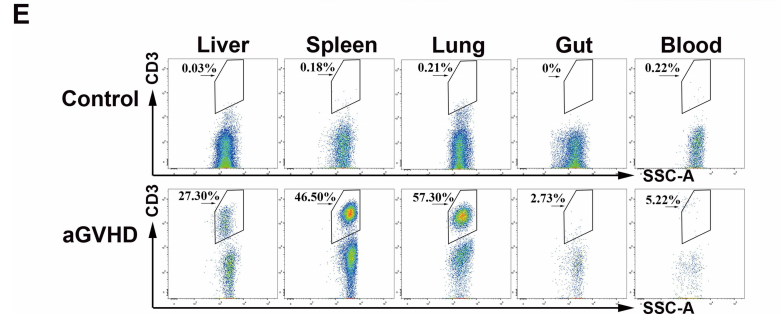
Fig2. The GVHD response of HuPBMC-NPG
NPG mice aged 8-10 weeks were randomly divided into 2 groups (n=6/group) according to their body weight. control was given PBS treatment, and mice in the aGVHD group were irradiated and then injected with 3×106 PBMCs/mouse in the tail vein, and observed for growth and scored. aGVHD group showed weight loss, hunching, fur ruffling, decreased mobility, and diarrhea, and scores were significantly increased; similar to humans, NPG mice with aGVHD exhibited severe inflammation, leukocyte infiltration, necrosis, and tissue damage in target organs such as the liver, spleen, lungs, and intestines, with infiltration of brown mass-like PBMCs.
Efficacy studies in HuPBMC-NPG mice
1. The efficacy of human amniotic membrane mesenchymal stem cells (hAMSCs) in aGVHD mice[1]
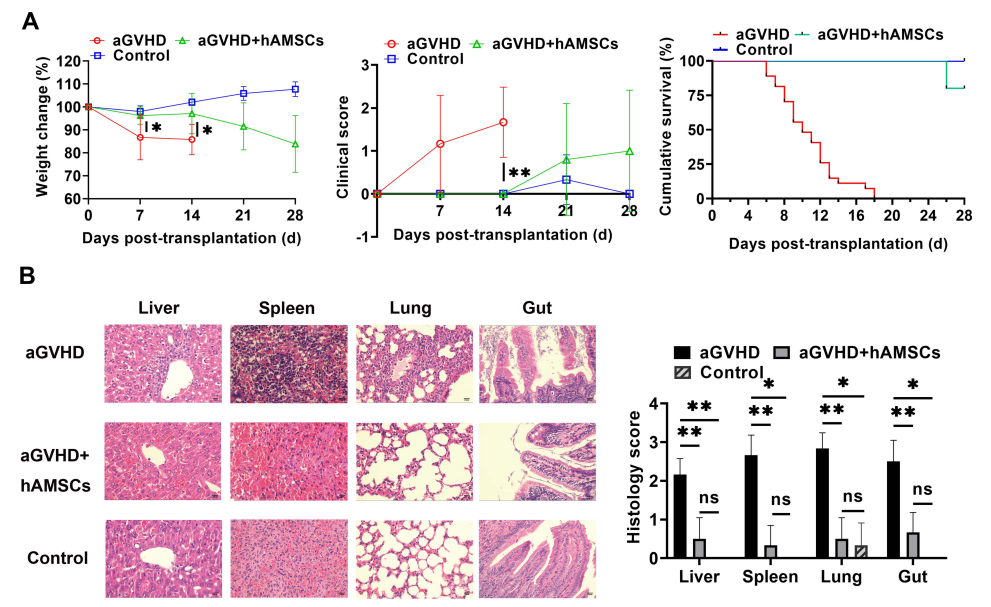
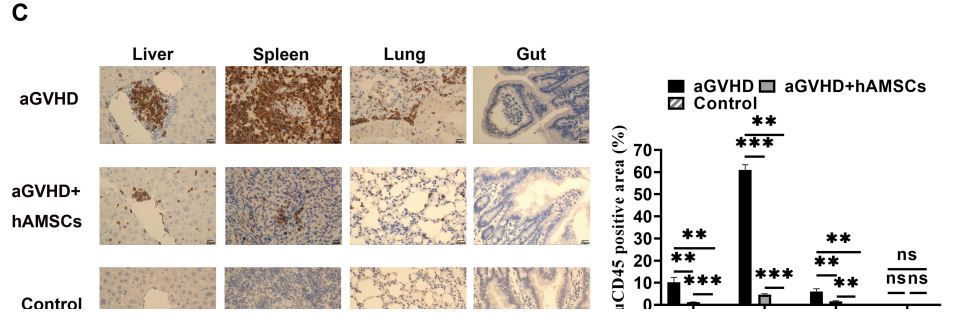
Fig3. Inhibition of aGVHD by hAMSCs in vivo
Both of aGVHD group and hAMSCs treatment group induced the development of aGVHD. aGVHD group mice were injected with PBS in the tail vein on day 3, and hAMSCs treatment group mice were injected with 5×105 hAMSCs in the tail vein. Con group were untreated. The results showed that hAMSCs significantly ameliorated the severity of acute GvHD in terms of weight loss and disease scores, blocked leukocyte infiltration, and reduced pathological changes in the liver, spleen, lungs, and intestines.
HuPBMC-NPG Mice Applications
1. Human-derived tumor cells, tumor tissue transplantation (CDX, PDX)
2. Research on the mechanism of GVHD and drug development to reduce GVHD response
3. Hematologic research (e.g., AIDS and other infectious diseases of the blood system)
4. Tumor immunity research, including tumor microenvironment research, immunomodulators, bispecific antibodies, immune cell relay therapy, tumor vaccines and other immunological methods of cancer treatment research
5. Gene therapy research
Reference
1. Gao Y, et al. Human Amniotic Mesenchymal Stem Cells Inhibit aGVHD by Regulating Balance of Treg and T Effector Cells. J Inflamm Res. 2021, 14:3985-3999.

 animalmodel@vital-bj.com
animalmodel@vital-bj.com +8610-84928167
+8610-84928167