General Information
Strain Name | B6-Mc4rem1/Vst |
Common Name | Mc4r KO; C57BL/6-Mc4r KO |
Origin | Beijing Vitalstar Biotechnology Co., Ltd. |
Background | C57BL/6NCrl |
Coat color | Black |
Edited Gene | Mc4r |
Development
Mc4r (melanocortin 4 receptor) is a protein-coding gene. Using CRISPR-Cas9 technology, all coding sequences of the Mc4r gene were deleted from C57BL/6NCrl mice to obtain Mc4r KO mice first established mice. Then, following the method of strain establishment, a core group was obtained, embryonic liquid nitrogen preservation was performed, and a production group was established.
Mc4r KO (purebred) mice weighed up to 30 g at 6-8 weeks and exhibited significant obesity. Mc4r KO mice fed in combination with high-fat (HFD-fed) exhibited hepatic steatosis (8-20 weeks), hepatic fibrosis (8-20 weeks), and hepatocellular carcinoma (12 months), similar to models characterized by the human NASH model. Cholesterol 140-160 mg/dl; (high-fat diet >300 mg/dl)
Phenotype
1. Weight and appearance[1]
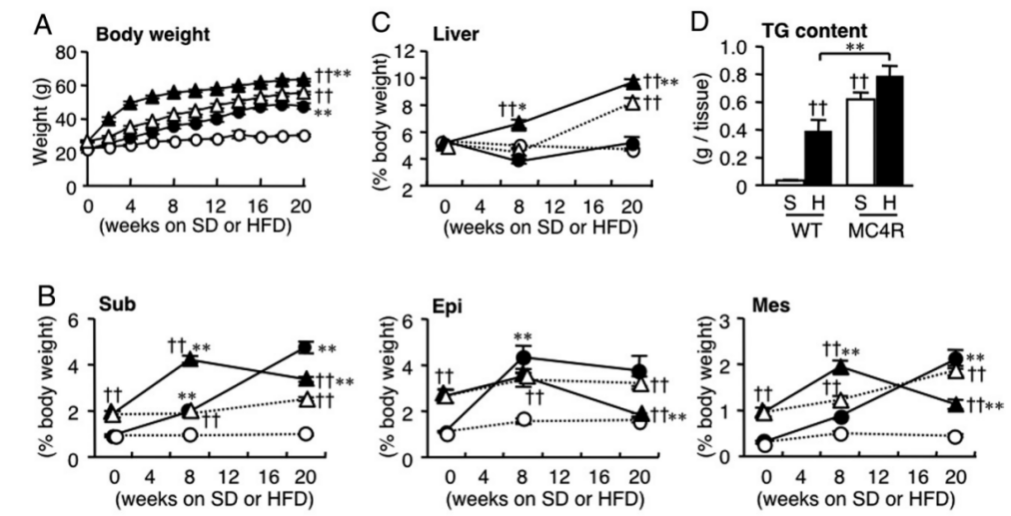
Fig. 1. Apparent and body weight of Mc4r KO mice induced by DIO dietary induction
Note: WT+SD for hollow circles, WT+HFD for solid circles, Mc4r KO+SD for hollow triangles, and Mc4r KO+HFD for solid triangles.
Animals: Mc4r KO mice on the C57BL/6J background
Diet: normal maintenance diet (SD), 60% high fat diet HFD (D12492; 524 kcal/100 g, 60% energy as fat)
METHODS: 8-week-old male mice were fed ad libitum water and standard diet for 20 weeks.
A: growth curve
B: Subcutaneous (Sub), epididymal (Epi), mesenteric (Mes) white adipose tissue weights
C: liver weight
D: liver TG content at 20 weeks
The results showed that Mc4r KO showed greater weight gain after feeding either SD or HFD diets, indicating the successful establishment of a high-fat diet-induced obese mouse model.
2. Serologic parameters in Mc4r KO mice fed HFD for 20 weeks[1]
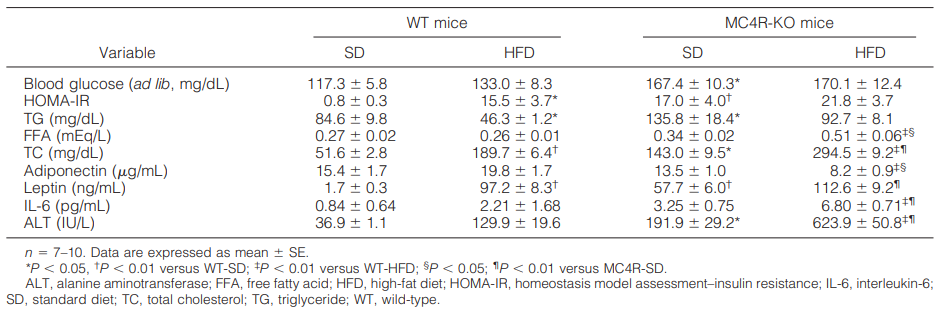
The results showed that both genotypes of mice fed HFD exhibited insulin resistance, and serum alanine aminotransferase concentrations were significantly increased in Mc4r KO mice fed HFD compared to any other group. Overall, Mc4r KO mice fed HFD exhibited metabolic profiles similar to those of obese humans.
3. Mc4r KO H&E staining of liver sections, Masson's trichrome staining method with Sirius red staining[1]
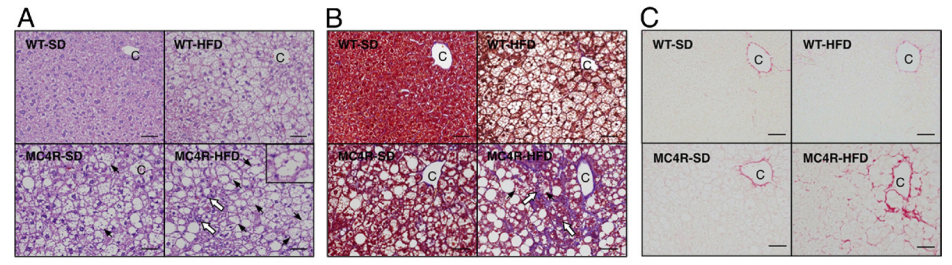
Fig 2. Histological analysis of the liver of Mc4r KO mice fed HFD for 20 weeks
After 20 weeks of HFD feeding, the livers of WT mice uniformly showed microvesicular steatosis and a moderate inflammatory cell infiltrate, and liver fibrosis was rarely observed at this time point. In contrast, the livers of Mc4r KO mice fed HFD exhibited microvesicular and macrovesicular steatosis, ballooning degeneration, and a large inflammatory cell infiltrate. Masson's trichrome and Sirius red staining showed marked pericyte fibrosis in the livers of Mc4r KO mice fed HFD.
4. Epistasis information for Mc4r KO mice

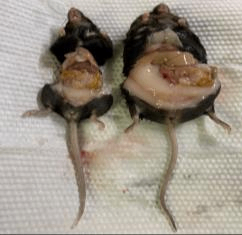
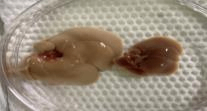
A B C
Fig3. Epistasis information for Mc4r KO mice
Note: A: WT on the far right, three on the left are Mc4r KO mice; B: Typical anatomical view; C: Typical liver view
Examples of Mc4r KO mouse studies
1. Preclinical pharmacodynamics Mc4r KO evaluation
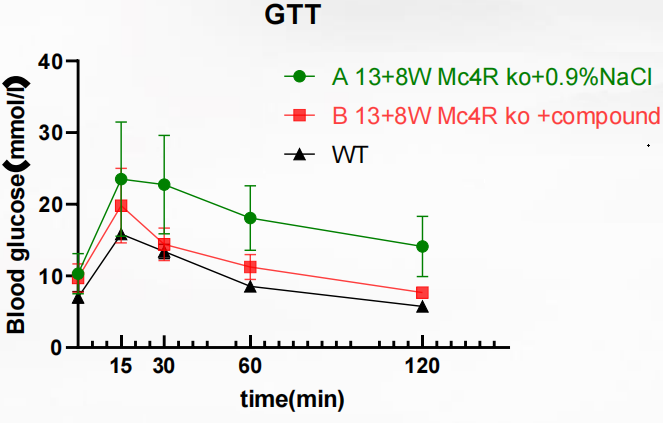
Fig 4. glucose tolerance test (GTT)
The results showed that impaired glucose tolerance was present in the Mc4r KO + compound group, but the tolerance was mild compared to the Mc4r KO + 0.9% NaCl group. It was confirmed that compound may regulate blood glucose through the insulin signaling pathway, and consequently, Mc4r KO can be used as a valid model for pharmacological glucose tolerance test.
Mc4r KO Mice Applications
1. Diabetes and Obesity Research
2. Obesity with Diabetes Study
3. Metabolic defects
4. Hyperinsulinemia
5. Neurobiology Research
6. High-fat-induced MASH modeling
References
1. Itoh M, et al. Melanocortin 4 receptor-deficient mice as a novel mouse model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Am J Pathol. 2011, 179(5):2454-2463.

 animalmodel@vital-bj.com
animalmodel@vital-bj.com +8610-84928167
+8610-84928167