General information

Development
The B2m gene encodes β2 microglobulin, a subunit of the MHC class I molecules. MHC class I molecules play a significant role in T cell responses during xenogeneic rejection reactions. After the knockout of the B2m gene, the surface of the mice no longer expresses MHC class I molecules, and the graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) caused by human-derived immune cells attacking mouse cells after human PBMC transplantation is significantly reduced. The onset of GvHD is delayed from an
average of 3-4 weeks post-transplantation to an average of 6-8 weeks. To this end, CRISPR-CAS9 technology was used to delete 674 base pairs of the MHC class I subunit B2m (beta-2 microglobulin) gene, including the 2nd exon and adjacent intron of NPG mice, resulting in B2m gene knockout NPG mice.
The homozygous knockout mice for B2m have little expression of MHC class I proteins on the cell surface. In the absence of CD8+ cytotoxic T cells, CD4+ cytotoxic T cells will compensatorily increase. The severe lack of CD8+ cytotoxic T cells in the immune response provides a way to evaluate the role of CD8+ T cells and MHC class I proteins in various immune reactions. Using NPG B2m mice to establish a humanized mouse model with PBMCs can provide a longer experimental window period than the PBMC model in NPG mice, offering a mouse model for studying the in vivo mechanisms of xenogeneic GvHD and evaluating corresponding therapeutic drugs, thus making it a more ideal humanized mouse model with significant application value in tumor immunology research.
Phenotype
1. Reconstitution of human PBMC transplanted in NPG-B2m mice
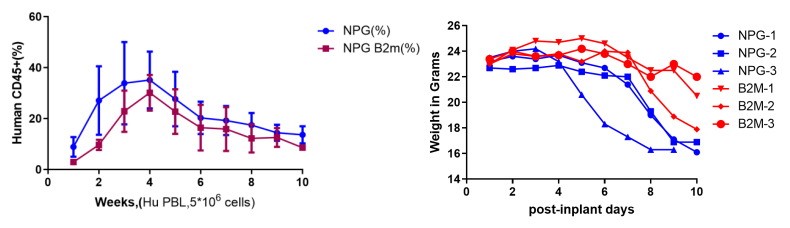

Fig1. Body weight profiles, body condition and reconstruction levels of NPG and NPG-B2m mice inoculated with Hu-PBMC (5×106)
NPG and NPG-B2m transplantation of Hu-PBMC cells delayed the GvHD response in DK-NPG mice compared to NPG mice. As shown, GvHD did not occur 5 w after NPG-B2m transplantation of PBMC (left side) and GVHD appeared 5 w after NPG transplantation of PBMC (right side).
NPG-B2m tumor modeling case
1. Construct a human lung cancer model and study the transplantation of Hu-PBMC
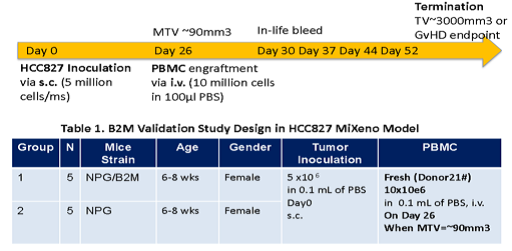
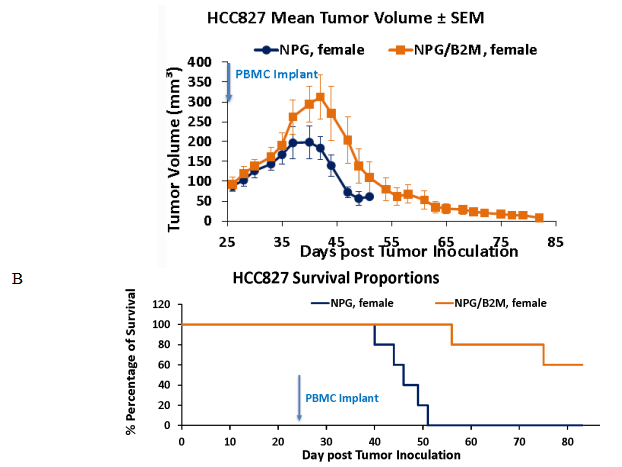
Fig2. Efficacy of transplanting Hu-PBMC in NPG-B2m mice with HCC827 tumor model
6-8 week-old female NPG and NPG-B2m mice (n=5 per group) were subcutaneously injected with HCC827 cell line. When the tumors grew to 90 mm3, Hu-PBMCs were administered. Continuous observation was conducted, and the results showed that the survival period of B2m-NPG mice was significantly prolonged, and the transplanted donor PBMCs had a certain tumor-suppressing effect.
NPG-B2m Mice Applications
1. in vivo mechanism study of GVHD in xenografts
2. Inoculation of human tumors or tissues for the screening of relevant drugs, such as tumor immunity antibody drugs, CAR-T efficacy studies, etc.
3. Preparation of humanized mouse models of the immune system, e.g. humanized mouse models of the immune system obtained by inoculation with PBMC or HSC
4. Human hematopoietic system and immune system research
Reference
1. Shultz LD, Schweitzer PA, Christianson SW, et al. “Multiple defects in innate and adaptive immunologic function in NOD/LtSz-scid mice”. J. Immunol. 1995, 154: 180-191.
2. King MA; Covassin L; Brehm MA; et al. 2009. Human peripheral blood leucocyte non-obese diabetic-severe combined immunodeficiency interleukin-2 receptor gamma chain gene mouse model of xenogeneic graft-versus-host-like disease and the role of host major histocompatibility complex. Clin Exp Immunol, 2009, 157(1):104-18.

 animalmodel@vital-bj.com
animalmodel@vital-bj.com +8610-84928167
+8610-84928167