General Information
Strain Name | KPA mice |
Common Name | LSL-KrasG12D/+;Ptenflox ;Alb-Cre/Alb-CreERT2 |
Origin | Beijing Vitalstar Biotechnology Co.,Ltd. |
Background | B6.129 |
Coat Color | Black & agouti |
Development
The pcDNA3.1-Alb-Cre and Alb-Cre ERT2 linearized fragments were injected into pronuclei of C57BL/6NCrl embryo respectively, and transgenic positive mice were obtained. After mating with ROSA26-reported mice (ROSA26-CAG-LSL-tdTOMATO), the mouse with tdTOMATO fluorescence in the total liver region was selected as the founder mouse to obtain the correct expression of Alb-Cre and Alb-Cre ERT2.
Alb-Cre/Alb-CreERT2 mice were mated with LSL-KrasG12D/+ and Ptenflox mice to obtain LSL-KrasG12D/+; Pten flox; Alb-Cre /Alb-CreERT2 mice (KPA/KPAER mice) , LSL-KrasG12D/+; Pten flox/flox; Alb-Cre /Alb-CreERT2 mice (KPPA/ KPPAER mice) , and LSL-KrasG12D/+;Alb-Cre /Alb-CreERT2 mice (KA/KAER mice) . The KPPA mice showed apparent growth retardation and started to demonstrate abdominal distension at ~5 weeks of age, frequently accompanied by jaundice and weight loss. It is noteworthy that homozygous Pten deletion in cooperation with oncogenic Kras mutation induces ICC (intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma) exclusively. KPA and KA mice also developed liver tumors at 6~7 and 12~18 months, respectively.
KPPAER mice were injected with TMX at eight weeks after birth and multiple liver tumors were observed three months later. Histological analyses showed that all tumors were HCC (hepatocellular carcinoma) and HD (hepatocellular dysplasia) but not ICC. KPPAER mice were injected with TMX at postnatal day 10 (P10) and these mice developed ICCs exclusively,which phenocopied the KPPA mice[1].
Phenotype
1.The liver tumors photos of KPPA mice
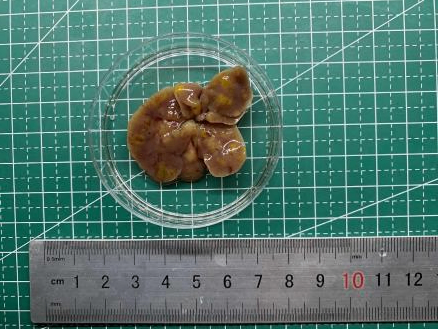
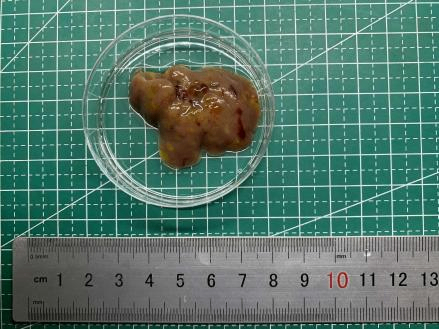
Fig 1. Gross appearance of an KPPA mouse at 5 weeks of age. Diffuse and firm tumorous lesions were observed in the liver.
2. H&E staining of the liver tumors
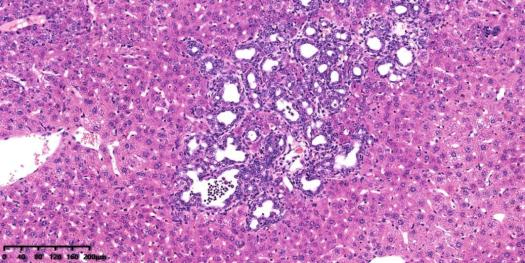
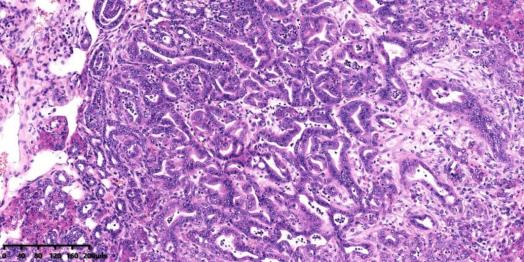
4× magnification 10× magnification
Fig 2. H&E staining of the liver of the KPPA mice at 5 weeks
The HE staining of the liver tumor shows that various degrees of hyperplasia in the bile ducts, characterized by increase in number and size, and change in morphology, invasive tumors were apparent with an abundant desmoplastic stroma, or “desmoplasia” .The tumors primarily showed glandular morphology that resembled well-differentiated human ICC.
Reference
1. Ikenoue T, Terakado Y, Nakagawa H, et al. A novel mouse model of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma induced by liver-specific Kras activation and Pten deletion. Sci Rep. 2016, 6:23899.

 animalmodel@vital-bj.com
animalmodel@vital-bj.com +8610-84928167
+8610-84928167