General Information
Strain Name | C57BL/6N-PD-L1emTg(CAG-hPD-L1)/VST |
Common Name | hPD-L1/PD-L1-/- |
Origin | Beijing Vitalstar Biotechnology Co., Ltd. |
Background | C57BL/6NCrl |
Coat Color | Black |
Related gene | PD-L1 |
Development
First, the CAG-hPD-L1 linearized fragment was injected into C57BL/6NCrl mouse embryonic prokaryotes to obtain hPD-L1-Tg-positive mice, which were constructed as in Fig 1.

Fig 1. schematic diagram of hPD-L1-Tg mouse construction
Secondly, PD-L1 gene knockout mice were created using sgRNA (single-guide RNA) to guide Cas9 nuclease to introduce double-strand breaks (DSBs) at specific sites in the DNA. The mice were targeted with the PD-L1-201 transcript, and the gene was cut at the 2nd intron and the 6th intron, then directly joined the two cuts using the NHEJ (Non-homologous end joining) repair pathway, and the exon3 to exon6 sequence was deleted to achieve the goal of knocking out the mouse PD-L1 gene.
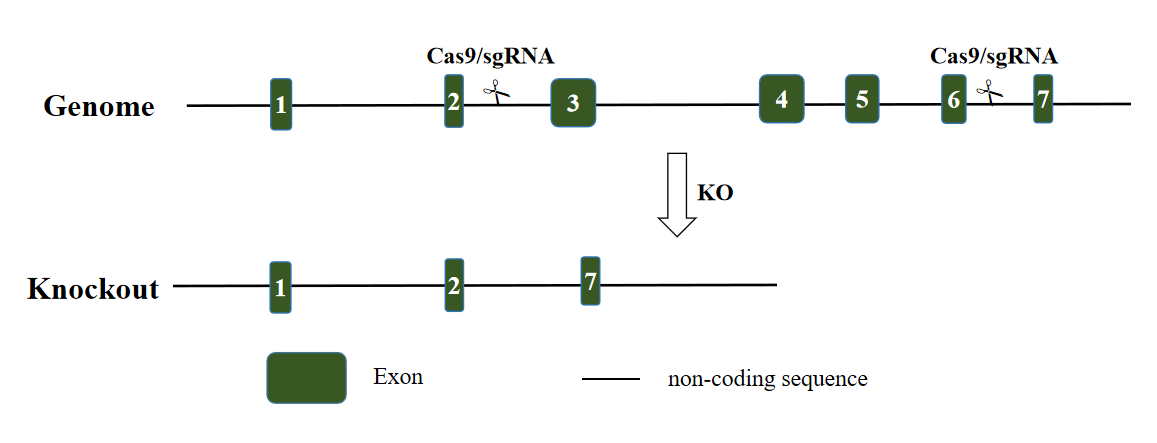
Fig 2. Schematic diagram of PD-L1 knockout mouse construction
By phenotypic analysis, hPD-L1-Tg-positive mice were selected for mating with PD-L1 knockout mice to obtain hPDL-1/mPDL-1-ko mice (C57BL/6N-PD-L1emTg(CAG-hPD-L1)).
Genotype identification information
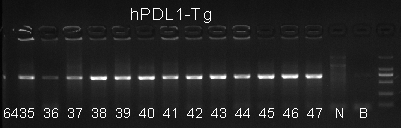
Fig 3. Identification of hPD-L1 random transgenic mouse
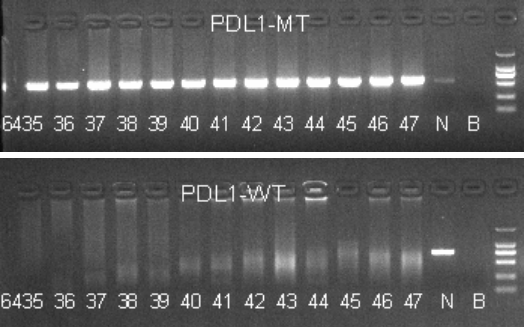
Fig 4. Identification of PD-L1 knockout mice
hPD-L1 Mice Applications
1. PD-L1 targeted drug development and screening
2. Evaluation of efficacy and safety of PD-L1-targeted drugs
3. Evaluation of tumor immunotherapy
4. Research on immune system and tumor immune escape mechanism
5. Tumor therapeutic effects of human PD-L1 inhibitors

 animalmodel@vital-bj.com
animalmodel@vital-bj.com +8610-84928167
+8610-84928167