Atherosclerosis is a chronic artery disease characterized by the formation of atherosclerotic plaques in the inner lining of the artery wall, leading to narrowing of the artery lumen and obstruction of blood flow. This lesion usually occurs in large and medium-sized arteries, such as the coronary arteries, carotid arteries, aorta, and lower limb arteries, and is one of the leading causes of cardiovascular disease, such as heart disease and stroke. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis usually goes through the following stages: endothelial damage: high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking and other factors cause endothelial cell damage; Lipid deposition: Low density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol accumulates under the endoderm, forming lipid streaks; Inflammatory response: Endothelial injury and lipid accumulation lead to inflammatory response, monocytes enter the artery wall and transform into macrophages, engulf oxidized LDL, and form foam cells; Plaque formation: Foam cells, smooth muscle cells, and other cells accumulate under the endoderm to form atherosclerotic plaques covered with fibrous caps; Plaque instability: Over time, plaque may rupture, leading to the formation of blood clots that further block blood vessels.
Vitalstar has developed the Apoe KO model and Ldlr KO model, which can be used in the research of atherosclerosis and can provide drug efficacy studies.
(1)Ldlr KO model and its drug efficacy evaluation
1. Experimental scheme
Ldlr KO mice were fed a high-fat diet (HFD), which usually lasted for 12-16 weeks at the time of modeling and could be adjusted for experimental purposes.
2. Experimental data
Blood lipid levels: total cholesterol (TC), low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), triglyceride (TG); Analysis of atherosclerotic lesions. Lipid plaque area was assessed by oil red O staining of the aorta and aortic arch. Paraffin embedding, section, HE staining and Masson staining were performed on the fixed aorta and heart tissues to observe the plaque structure and fibrosis degree.
(2)Apoe KO model and its drug efficacy evaluation
1. Experimental scheme
Apoe KO mice were fed a high-fat diet (HFD), which usually lasted for 12-16 weeks at the time of modeling and could be adjusted for experimental purposes.
2. Experimental data
Lipid levels: TC, LDL-C, HDL-C, TG; Analysis of atherosclerotic lesions. Lipid plaque area was assessed by oil red O staining of the aorta and aortic arch. Paraffin embedding, section, HE staining and Masson staining were performed on the fixed aorta and heart tissues to observe the plaque structure and fibrosis degree.
Case 1
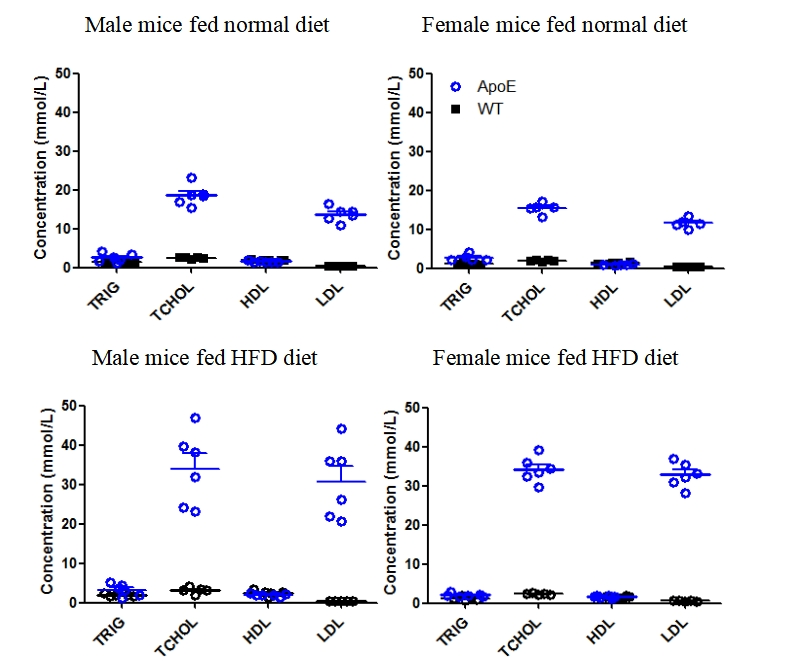
Fig1. Serum lipids detection of wild-type mice and Apoe KO mice.
TRIG: Triglyceride; TCHOL: Total Cholesterol; HDL: High-density lipoprotein; LDL: Low Density Lipoprotein.
Mice of different genders were randomly divided into two groups. Starting from the age of 4 weeks, one group was fed ordinary diet and the other group was fed high-fat diet. After feeding for 10 weeks, venous blood of mice was collected to detect the related indexes of lipids. Figure 3 shows that the concentrations of triglycerides and low-density lipoproteins in Apoe KO mice were significantly higher than those in wild-type mice regardless of whether they were fed high-fat diet or ordinary diet. The concentrations of triglyceride and low density lipoprotein of Apoe KO mice fed with high fat diet were higher than those of Apoe KO mice fed with ordinary diet.
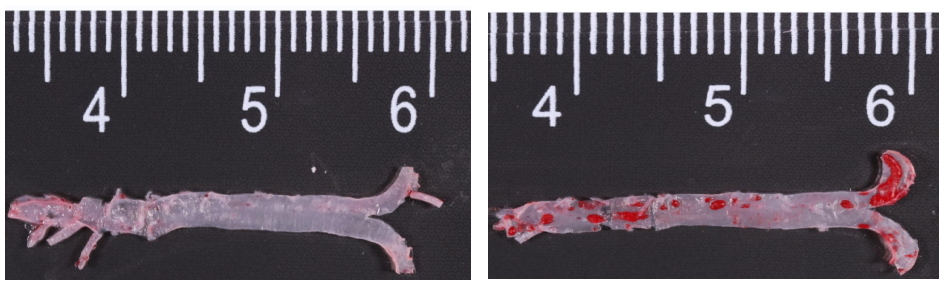
Fig2. Oil red O staining of the aorta. Left: Control mice on normal diet; Right: Apoe KO mice on HFD
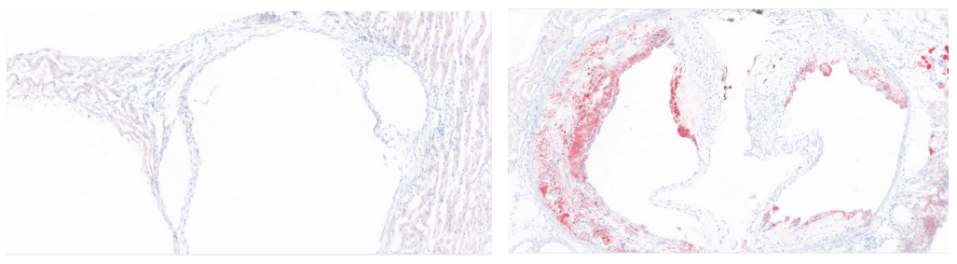
Fig 3. Oil red O staining of the aortic root. Left: Control mice fed normal diet; Right: Apoe KO mice fed HFD.

 animalmodel@vital-bj.com
animalmodel@vital-bj.com +8610-84928167
+8610-84928167