Tumor immune dual-humanized mouse models typically refer to the implantation of human tumor cells and human immune systems in immunodeficient mice, creating a research platform that includes both human immune systems and tumors. This model has higher clinical relevance, diversity, and flexibility.
Better clinical relevance is demonstrated by the fact that compared to traditional tumor xenograft models, dual-humanized models include the human immune system, making the research results more clinically relevant. Secondly, it allows for the study of more complex tumor-immune interactions, providing a more comprehensive understanding of tumor biology and immune mechanisms. Diversity and flexibility are reflected in its applicability to the study of various tumor types and immunotherapies, offering a flexible research platform. At the same time, different tumor and immune cell types can be selected according to research needs, customizing the research model.
Our independently developed tumor immune dual-humanized mouse model provides a powerful tool for cancer research, capable of more accurately simulating the interactions between human tumors and the immune system, offering an important platform for the development of immunotherapies, drug screening, and personalized medicine research.
(1)Rich experience in tumor immune dual-humanized xenograft tumor models
1. Constructing human gastric cancer model and evaluating therapeutic effect of gastric cancer mesenchymal stem cells combined with PD-1 antibody[1]
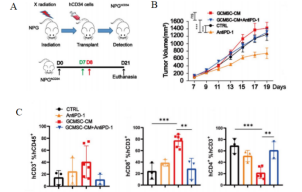
Fig1. Tumor and tumor tissue immune cell levels after HuHSC-NPG inoculation of gastric cancer tumors
4-8 week-old NPG mice were irradiated with X-rays (1.2 Gy) and within 24 hours intravenously injected with 5×104 human umbilical cord blood CD34+ cells. After 12 weeks of reconstitution, patient-derived gastric cancer cell lines were inoculated, and treated with GCMSC-CM and PD-1 antibody alone or in combination to observe tumor changes, and to detect the levels of CD45+CD3+, CD3+CD8+, and CD3+CD4+ in tumor tissues from different treatment groups. The results showed that after 21 days of treatment, PD-1 antibody therapy significantly inhibited gastric tumor growth, while the combination of GCMSC-CM with PD-1 antibody significantly increased tumor volume compared to PD-1 antibody alone, indicating that GCMSC-CM negated the inhibitory effect of PD-1 antibody on gastric tumor growth.
2. Constructing human lymphoma model and evaluating the efficacy of small molecule inhibitors[2]
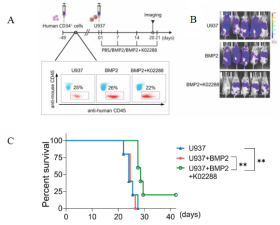
Fig2. Schematic diagram of HuHSC-NPG inoculated U937 cell construction and anti-tumor effect
Female NPG mice (n=5 per group) at 5-6 weeks of age were irradiated (1 Gy) with 5×105 human CD34+ cells injected into the tail vein after marrow clearing, and the peripheral blood was assayed for antibodies against anti-mouse CD45 and anti-human CD45 after 6-7 weeks. The proportion of human CD45+ cells in the peripheral blood mononuclear cells of mice was > 20%, confirming the success of human leukocyte transplantation. U937 with BMP2 or BMP2 with k02288 were injected as shown. aiming at hindering the tumor growth effect of Reg-Vδ2 T cells by inhibiting the BMP2 signaling pathway through small molecule inhibitors. The results showed that k02288 combined with BMP2 treatment then significantly inhibited the growth and significantly prolonged the survival of U937 cells.
Reference
[1] Huang C, Chen B, Wang X, et al. Gastric cancer mesenchymal stem cells via the CXCR2/HK2/PD-L1 pathway mediate immunosuppression. Gastric Cancer. 2023, 26(5):691-707.
[2] Liang S, Dong T, Yue K, et al. Identification of the immunosuppressive effect of γδ T cells correlated to bone morphogenetic protein 2 in acute myeloid leukemia. Front Immunol. 2022, 13:1009709.

 animalmodel@vital-bj.com
animalmodel@vital-bj.com +8610-84928167
+8610-84928167